Are you ready for the electronic Bill of Lading (eBL)?
Join an eBL platform today


eBL solution providers are supporting the shipping industry and driving the adoption of DCSA’s global standards by offering digital platforms that enable the secure issuance, transfer, and management of eBLs. Now, with the establishment of eBL platform interoperability, these platforms are unlocking even more of eBL’s potential—enhancing efficiency, security, and enabling industry-wide scalability. Watch the video for more details.
What is eBL Platform Interoperability?
eBL platform interoperability enables electronic bills of lading (eBLs) to be exchanged seamlessly across different digital platforms, regardless of the solution provider. This ensures that all stakeholders—shippers, carriers, banks, and regulators—can securely access, verify, and process eBLs without being restricted to a single system. This not only improves operational efficiency and security but also drives broader adoption of digital trade documentation, paving the way for a truly connected global trade ecosystem.
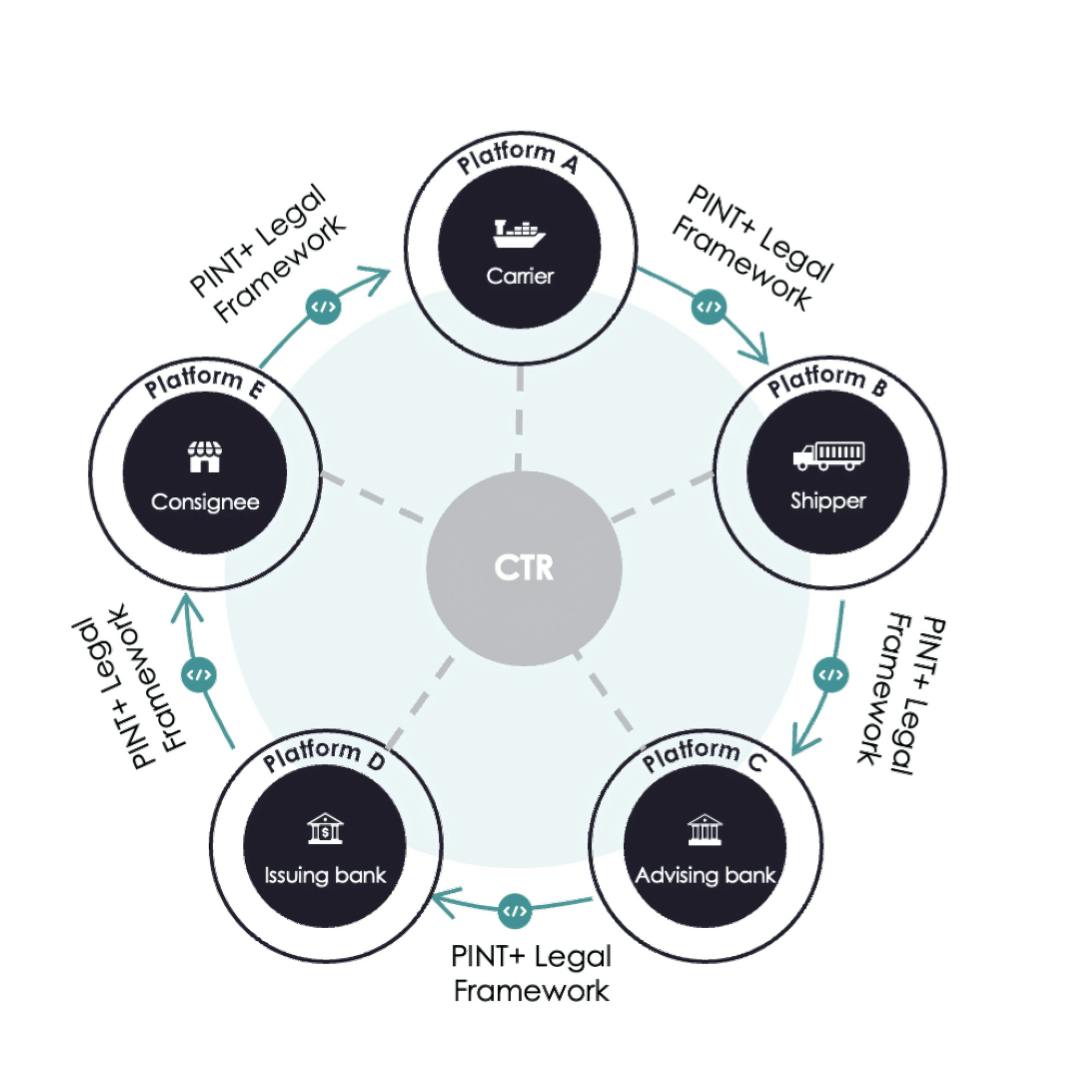
How eBL Platform Interoperability works
eBL platform interoperability is achieved through three key components:
- Platform Interoperability (PINT) API – A standardized bilateral integration between all eBL solution providers, enabling the transfer of DCSA standards-compliant electronic bills of lading (eBL) along with additional documentation.
- Legal Framework (MSPIA + Standard Annex) – The Multilateral Service Provider Interoperability Agreement (MSPIA) ensures a standardized legal framework to govern the relationaship between eBL solution providers. The Standard Annex, combined with the existing terms of the individual platforms, regulates the relationship between users.
- Control Tracking Registry (CTR) – A service that provides a real-time record of the platform where a specific interoperable eBL is controlled.

Getting started with interoperable eBL
- Onboard on an eBL platform – Each user receives a unique identifier. The equivalent of a bank account number , but for eBLs.
- Agree to the legal terms and Standard Annex – Users must accept these terms for eBL interoperability.
- Obtain the unique identifier of the counterparty – For example, an ocean carrier should obtain the shipper's identifier, and a shipper should obtain the consignee's identifier.
- Transfer the eBL – The platform facilitates the transfer.
- Interoperable eBL exchange – The platform creates an “eBL envelope” and transfers the eBL via the PINT API while updating the CTR to track where the eBL is being controlled.
Frequently Asked Questions
To gain a deeper understanding of the benefits of eBL Platform Interoperability and to explore the next steps, contact one of our experts.
